BYO Modem Setup Guide
- Aug 22
- 3 min read
Updated: 6 days ago
Your nbn® service is now active — great news! Before you can jump online, stream movies, or get back to work, you’ll need to configure a compatible modem or router.
The good news? Setting up your own (BYO) equipment is usually simple. This guide provides the recommended settings for each type of nbn® technology. Router menus can vary, so we’ll keep this page updated with the most important information.
If your device or interface isn’t covered here, let us know and we’ll do our best to add it.
Sections in this guide:
Common router login addresses
Most routers are accessed by typing an IP address (or web link) into your browser’s address bar. The defaults vary by brand:
Asus: 192.168.1.1
Billion: 192.168.1.254
D-Link: 192.168.0.1, http://dlinkrouter, or 192.168.1.1
Fritzbox: 192.168.178.1
Huawei: 192.168.1.1
Netcomm: 192.168.20.1 or http://cloudmesh.net/
Netgear: 192.168.0.1, 192.168.1.1, or http://routerlogin.com
Sagemcom F@st: 192.168.0.1, 192.168.1.1, or 10.1.1.1
Technicolor: 192.168.1.254
TP-Link: 192.168.1.1 or http://tplinkmodem.net
💡 Tip: If these don’t work, check the label on your router. If you’ve forgotten the admin password, press and hold the reset button on the back of the device for 8–10 seconds until the lights flash. This will restore factory defaults.
Fibre to the Node (FTTN) and Fibre to the Building (FTTB)
FTTN/FTTB services use your existing phone wall socket and require a VDSL2-capable modem/router. Older ADSL or VDSL1 hardware will not work.
Plug a grey or beige telephone cable (RJ11) from the wall socket into the port marked DSL on your modem/router.
👉 If using an Asus modem, configure the software before inserting the DSL cable.
Quick Settings – FTTN/FTTB
Option | Recommended Value |
DSL Mode / Interface | VDSL |
Internet Type | Dynamic / IPoE / DHCP |
VLAN ID | None |
IP Address | Obtain Automatically |
Username & Password | Not required |
SRA | Enable (if available) |
ISP Selection | Choose “Other” or “Not Listed” if asked |
FTTP, FTTC, HFC, and Fixed Wireless
These services use an nbn® connection device (also called an NTD or modem box) installed in your premises. Your router must connect to this unit via its WAN port.
If you’re on FTTP or Fixed Wireless and are moving from another provider, we’ll let you know which UNI-D port to use on the nbn® device — there may be more than one.
Quick Settings – FTTP / FTTC / HFC / Fixed Wireless
Option | Recommended Value |
WAN Interface | Ethernet WAN |
Internet Type | Dynamic / IPoE / DHCP |
VLAN ID | None |
IP Address | Obtain Automatically |
Mode | Wireless Router Mode (on TP-Link and similar) |
Final Steps
Save your configuration and apply the changes.
Power the modem/router off for about 10 minutes, then turn it back on.
Check if you can browse the internet.
If it still doesn’t connect, give our support team a call on 1300 372 000.
Troubleshooting
Still no internet? Work through these checks:
Make sure all cables are connected securely (DSL, Ethernet, and power).
Restart your nbn® device (NTD) by switching it off for 1–2 minutes.
Double-check you’re connected to the right port (DSL for FTTN/FTTB; WAN/UNI-D for FTTP, FTTC, HFC, and FW).
If unsure about your router’s setup, reset it to factory settings and start again.
Try powering off both the modem/router and nbn® device for 10 minutes, then power them back on.
If none of the above work, contact our help desk on 1300 372 000.
Router Setup Examples (with Screenshots)
Below are examples of what the settings pages look like for the most common router brands. Click to enlarge.
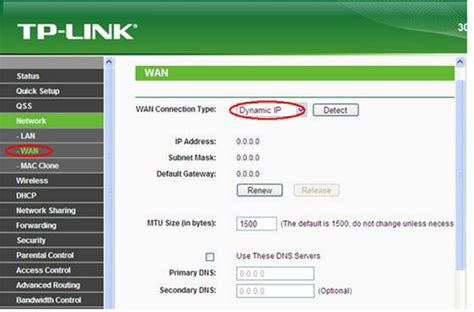
TP-Link
Go to Network > WAN
Connection Type = Dynamic IP
VLAN ID = None
Operation Mode = Wireless Router Mode (if available)
📸 Example:
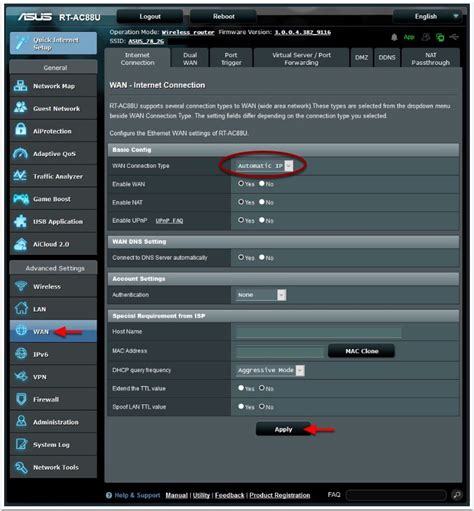
Asus
Go to Advanced Settings > WAN > Internet Connection
WAN Type = Automatic IP
DSL Modulation = VDSL2 (only if FTTN/FTTB)
Username & Password = leave blank
📸 Examples:
Netgear
Go to Advanced > Setup > Internet Setup
Does your Internet require a login? = No
IP Address = Get Dynamically from ISP
VLAN/IPTV = Disabled
📸 Example:

